Rabbits are captivating creatures that have captured the hearts of pet owners worldwide. Understanding their dietary needs is crucial for their well-being and longevity. This guide will delve into the fascinating world of rabbit nutrition, exploring the intricacies of their dietary requirements and providing practical tips for ensuring a healthy and balanced diet for your furry companion.
Rabbits possess unique digestive systems that necessitate a specific diet to thrive. Their primary food source is hay, which provides essential fiber for maintaining gut health. Pellets and vegetables complement hay, offering a balanced intake of nutrients. Understanding the factors influencing their food consumption, such as age, breed, and activity level, is essential for tailoring their portions to prevent underfeeding or overfeeding.
Dietary Needs of Rabbits
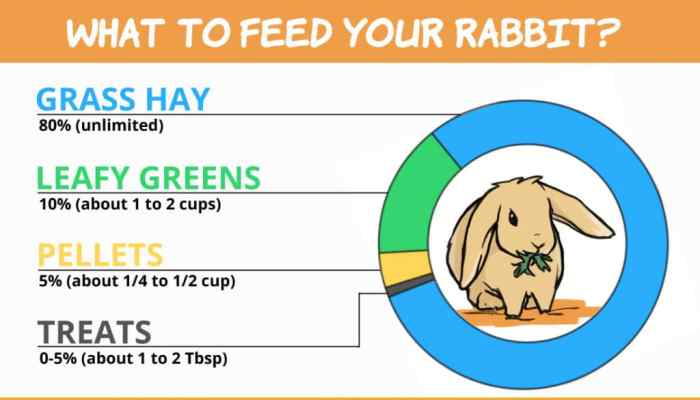
Rabbits are herbivores and their diet should consist mainly of hay, pellets, vegetables, and water. The specific nutritional requirements of rabbits vary depending on their breed, age, and health status. However, all rabbits need a diet that is high in fiber and low in protein and fat.
Hay
Hay is the most important part of a rabbit’s diet and should make up 80-90% of their daily intake. Hay provides rabbits with the fiber they need to maintain a healthy digestive system. It also helps to wear down their teeth, which are constantly growing.
The best type of hay for rabbits is timothy hay. Other good choices include orchard grass hay and oat hay. Alfalfa hay is high in protein and calcium, so it should only be fed to rabbits under 6 months old or to pregnant or nursing rabbits.
Pellets
Pellets are a good source of protein, vitamins, and minerals for rabbits. However, they should only make up 10-15% of a rabbit’s daily intake. Too many pellets can lead to obesity and other health problems.
When choosing pellets for your rabbit, look for a brand that is specifically designed for rabbits. The pellets should be made from high-quality ingredients and should not contain any artificial colors or flavors.
Vegetables
Vegetables are a good source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants for rabbits. However, they should only be fed in moderation. Too many vegetables can lead to digestive problems.
Good choices for vegetables for rabbits include:
- Carrots
- Celery
- Collard greens
- Dandelion greens
- Kale
- Parsley
- Spinach
Water
Water is essential for rabbits and should be available at all times. Rabbits should drink about 1 ounce of water per pound of body weight per day.
A balanced diet is essential for maintaining rabbit health. A diet that is too high in protein or fat can lead to obesity, heart disease, and other health problems. A diet that is too low in fiber can lead to digestive problems.
If you are unsure about what to feed your rabbit, talk to your veterinarian.
Factors Affecting Rabbit Food Consumption
The amount of food a rabbit consumes can vary significantly depending on several factors. Understanding these factors and adjusting feeding portions accordingly is crucial to prevent underfeeding or overfeeding, which can lead to health problems.
Age
- Younger rabbits have higher metabolic rates and require more food per pound of body weight compared to older rabbits.
- As rabbits age, their metabolism slows down, and they may require less food.
Breed
- Larger breeds of rabbits, such as Flemish Giants, typically eat more than smaller breeds, such as Netherland Dwarfs.
- The breed’s body size and weight influence its daily food intake.
Activity Level
- Active rabbits that spend a lot of time hopping, running, or playing will require more food than sedentary rabbits.
- Exercise increases energy expenditure, leading to a higher demand for calories.
Environmental Conditions
- Rabbits living in cold environments may need more food to maintain their body temperature.
- Rabbits experiencing stress or illness may also eat more or less than usual.
Hay as a Staple Food
Hay plays a pivotal role in a rabbit’s diet, providing essential nutrients, promoting dental health, and aiding digestion. It should be offered in unlimited quantities to ensure optimal well-being.
Different types of hay vary in nutritional value and suitability for rabbits. The following table provides an overview:
| Hay Type | Nutritional Value | Suitability for Rabbits |
|---|---|---|
| Timothy Hay | High in fiber, low in protein | Excellent for adult rabbits |
| Orchard Grass Hay | High in protein, moderate in fiber | Suitable for growing rabbits or lactating does |
| Alfalfa Hay | Very high in protein, calcium, and calories | Should be limited to young rabbits under 6 months old |
Choosing high-quality hay is crucial. Look for hay that is fresh, green, and free of mold. Avoid hay that is brown or dusty, as it may be low in nutrients or contain harmful bacteria.
Pellets and Vegetable Supplementation
In addition to hay, pellets and vegetables play a vital role in providing a balanced diet for rabbits. Pellets are specially formulated to provide essential nutrients, while vegetables offer a variety of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Pellets should be introduced gradually to prevent digestive issues. Start by offering a small amount daily and gradually increase the quantity over a week. The recommended daily intake of pellets varies depending on the breed and age of the rabbit.
Recommended Daily Intake of Pellets
| Rabbit Breed | Age | Daily Intake |
|---|---|---|
| Dwarf | Under 6 months | 1/4 cup |
| Dwarf | Over 6 months | 1/8 cup |
| Medium | Under 6 months | 1/2 cup |
| Medium | Over 6 months | 1/4 cup |
| Large | Under 6 months | 3/4 cup |
| Large | Over 6 months | 1/2 cup |
Vegetables should be introduced gradually and in moderation. Start with a small amount and increase the quantity over a week. Avoid giving too many vegetables at once, as this can lead to digestive upset.
Water Consumption and Hydration
Rabbits require constant access to fresh, clean water to maintain proper hydration. Dehydration can lead to serious health issues, so it’s crucial to ensure your rabbit has adequate water intake.
Signs of dehydration in rabbits include lethargy, dry skin, sunken eyes, and decreased urine output. To prevent dehydration, provide your rabbit with a water bottle or bowl that is easily accessible and clean regularly.
Average Daily Water Intake
The average daily water intake for rabbits varies depending on their breed and age:
| Breed | Average Daily Water Intake (ml/kg) |
|---|---|
| Small breeds (under 2.5 kg) | 50-100 |
| Medium breeds (2.5-5 kg) | 100-150 |
| Large breeds (over 5 kg) | 150-200 |
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, understanding the dietary needs of rabbits is paramount for their optimal health. By providing a balanced diet consisting of hay, pellets, vegetables, and water, and adjusting portions based on individual factors, you can ensure your rabbit thrives and enjoys a long, healthy life.
Remember, a well-nourished rabbit is a happy rabbit!
Q&A
What is the average daily hay intake for a rabbit?
Rabbits should have unlimited access to high-quality hay, as it provides essential fiber for their digestive system.
How often should I feed my rabbit pellets?
Pellets should be offered once or twice a day, with the amount varying depending on the rabbit’s age, breed, and activity level.
What types of vegetables are safe for rabbits?
Safe vegetables for rabbits include leafy greens (e.g., romaine lettuce, spinach), carrots, bell peppers, and broccoli. Introduce new vegetables gradually to avoid digestive issues.
How much water should my rabbit drink daily?
Rabbits should have access to fresh water at all times. The average daily water intake varies depending on factors such as age, breed, and environmental temperature.