Have you ever wondered if your furry friend can see the world in the same vibrant colors as you do? Rabbits are fascinating creatures with unique adaptations, including their vision. In this article, we’ll delve into the intriguing question: Are rabbits colorblind? We’ll explore the structure of rabbit eyes, the mechanisms of color perception, and the evolutionary factors that have shaped their vision.
By understanding their colorblindness, we can better appreciate their world and provide them with a stimulating environment that meets their visual needs.
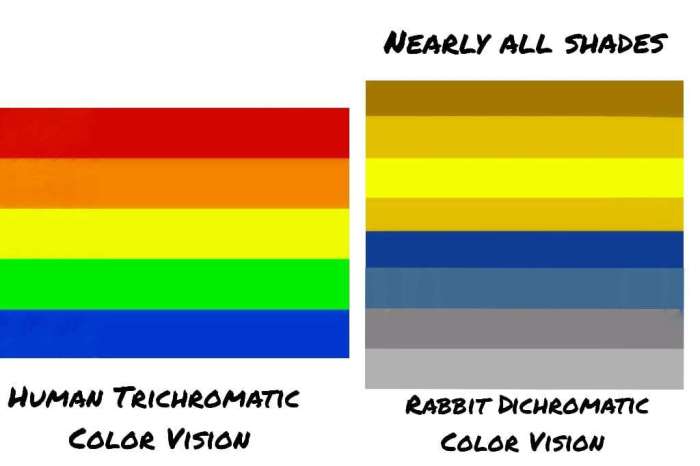
Rabbits possess eyes that are adapted to their lifestyle and environment. Their large, laterally positioned eyes provide them with a wide field of view, allowing them to detect predators and navigate their surroundings effectively. However, unlike humans who have trichromatic vision, rabbits have dichromatic vision, meaning they have only two types of cone cells in their retinas.
This limits their ability to perceive a full spectrum of colors compared to humans.
Rabbit Vision
Rabbits possess a unique visual system that enables them to perceive their surroundings effectively. Their eyes have adapted to their nocturnal and crepuscular lifestyle, allowing them to navigate and forage in low-light conditions.
The rabbit eye shares similarities with the human eye in terms of its basic structure. It comprises a cornea, pupil, iris, lens, retina, and optic nerve. However, there are key differences that contribute to the distinct visual capabilities of rabbits.
Visual Field
One notable difference between human and rabbit vision is their visual field. Humans have a binocular visual field, meaning they have overlapping fields of vision from both eyes, resulting in depth perception. In contrast, rabbits have a monocular visual field, with each eye having a separate field of vision.
This limited binocular overlap restricts their depth perception compared to humans.
Rods and Cones
The retina of a rabbit’s eye contains both rods and cones, similar to humans. Rods are responsible for low-light vision and are more sensitive to movement, while cones are responsible for color vision and are more sensitive to detail and color discrimination.
Rabbits have a higher proportion of rods to cones compared to humans, which enhances their ability to see in dim light.
Color Perception in Rabbits
Rabbits possess a unique visual system that enables them to perceive colors differently from humans. Unlike humans, rabbits are dichromats, meaning they have only two types of color receptors in their retinas. These receptors are sensitive to short wavelengths (blue-violet) and medium wavelengths (green-yellow), allowing rabbits to distinguish between these colors.
Color Spectrum
Rabbits have a limited color perception compared to humans. They can perceive a range of colors, including:
- Blue-violet
- Green-yellow
- Gray
- Black
- White
Rabbits cannot distinguish between red, orange, and yellow, as these colors fall within the range of wavelengths that their color receptors are not sensitive to. As a result, rabbits perceive these colors as shades of gray.
Evolutionary Adaptations
The evolution of rabbit color vision is closely tied to their ecological niche and survival strategies. Their limited color perception has been shaped by environmental factors and plays a significant role in their behavior and survival.
Rabbits are crepuscular, meaning they are most active at dawn and dusk. During these periods, the light is dimmer and dominated by shorter wavelengths, such as blues and greens. This limited color spectrum may have influenced the development of rabbit color vision, allowing them to distinguish objects and navigate their surroundings effectively in low-light conditions.
Color Perception and Survival
Rabbits’ limited color vision has several advantages for their survival. For instance, it allows them to better detect predators, which are often camouflaged in vegetation. The ability to differentiate between greens and blues helps rabbits identify potential threats and avoid becoming prey.
Additionally, their limited color perception enhances their ability to forage for food. Rabbits primarily consume plants, and their color vision allows them to distinguish between edible and inedible vegetation. They can easily spot green, leafy plants that are rich in nutrients while avoiding poisonous or toxic plants that may appear in different colors.
Examples of Color Vision in Natural Habitats
- In grassy environments, rabbits can distinguish between different shades of green, allowing them to locate patches of dense vegetation for cover or food.
- When foraging in forests, rabbits can detect the subtle differences in color between leaves and bark, helping them identify potential food sources and avoid predators that may blend into the surroundings.
- In alpine regions, rabbits’ color vision enables them to differentiate between snow and ice, preventing them from falling into treacherous areas.
Comparisons with Other Animals
Rabbits’ color vision differs from that of other mammals, including humans and dogs. Understanding these differences provides insights into their respective ecological niches and evolutionary adaptations.
Humans
- Humans possess trichromatic vision, meaning they can distinguish a wide range of colors, including red, green, and blue.
- This advanced color perception is advantageous for identifying ripe fruits, distinguishing between predators and prey, and navigating complex environments.
Dogs
- Dogs are dichromats, with color vision similar to that of rabbits.
- They can perceive blue and yellow, but struggle to distinguish between red and green.
- This limited color perception is sufficient for their ecological niche, as they rely more on scent and sound for hunting and social interactions.
Practical Implications
Rabbit colorblindness has significant implications for their interactions with humans, as well as for their veterinary care and environment.
Understanding their limited color perception allows us to make informed choices that enhance their well-being.
Toy and Environment Selection
When selecting toys for rabbits, it’s crucial to consider their colorblindness. Bright, saturated colors like red, orange, and yellow may not be as visually appealing to them as shades of blue, green, and violet.
Similarly, creating a stimulating environment for rabbits involves providing them with a variety of textures, shapes, and sizes of objects to explore.
Veterinary Care
Veterinarians need to be aware of rabbit colorblindness when conducting examinations and procedures.
For instance, using a red light during ophthalmic examinations may not be effective in detecting eye problems in rabbits, as they are less sensitive to this color.
Last Point
In conclusion, rabbits are indeed colorblind, possessing dichromatic vision that allows them to perceive a limited range of colors. This adaptation has evolved over time, influenced by their environment and survival needs. While they may not see the world in the same vibrant hues as we do, rabbits have developed exceptional visual adaptations that enable them to thrive in their natural habitats.
By understanding their colorblindness, we can provide them with appropriate care, toys, and environments that cater to their unique visual abilities.
FAQ
How does rabbit colorblindness affect their daily lives?
Rabbits rely on their vision for various activities, including predator detection, foraging, and social interactions. Their limited color vision may make it challenging to distinguish between certain colors, such as red and green, which can impact their ability to navigate complex environments.
Can rabbits see any colors at all?
Yes, rabbits can perceive a limited range of colors. They have two types of cone cells in their retinas, which allow them to see shades of blue and green. However, they are unable to distinguish between red and green, and they perceive these colors as shades of gray.
How can I choose appropriate toys and environments for my colorblind rabbit?
When selecting toys for your rabbit, opt for those in shades of blue and green, as these colors are more visible to them. Avoid using red or orange toys, as they may appear dull or gray to your rabbit. Similarly, create a stimulating environment with plenty of natural light and objects in shades of blue and green to enhance their visual experience.