Color vision is a fascinating aspect of animal biology that plays a crucial role in survival, communication, and overall well-being. Rabbits, with their distinctive appearance and unique characteristics, have sparked curiosity about their ability to perceive the world in color.
In this article, we delve into the captivating realm of rabbit color vision, exploring their visual capabilities and comparing them to other mammals. By unraveling the intricacies of their color perception, we gain insights into the evolutionary adaptations that have shaped their world.
Rabbits possess a unique visual system that allows them to navigate their surroundings effectively. Their eyes are positioned on the sides of their heads, providing them with a wide field of view. However, their color vision differs significantly from that of humans and other mammals, raising intriguing questions about their perception of the world around them.
Introduction
Understanding animal color vision is crucial for comprehending their perception of the world, communication, and survival strategies. Rabbits, as common and widely studied mammals, provide valuable insights into the diversity of visual systems in the animal kingdom.
Rabbits possess a unique visual system adapted to their nocturnal and crepuscular lifestyle. Their eyes are positioned laterally, providing them with a wide field of view for detecting predators and navigating their surroundings. However, their color vision capabilities have long been debated, with varying perspectives emerging from different studies.
Rabbit Color Vision
Color Vision in Rabbits
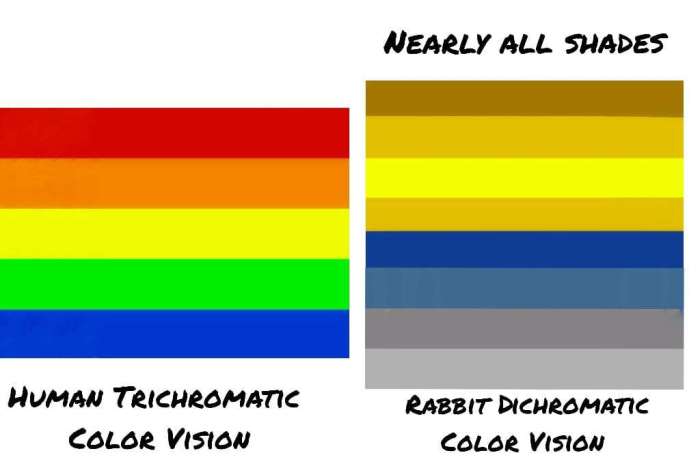
Rabbits have a unique type of color vision called dichromacy, which means they can only distinguish between two types of colors: blue-violet and yellow-green. This is different from humans, who have trichromatic vision and can distinguish between three types of colors: red, green, and blue.The
reason for this difference in color vision is due to the structure of the rabbits’ eyes. Humans have three types of cone cells in their retinas, which are responsible for detecting different colors of light. Rabbits, on the other hand, only have two types of cone cells, which means they are unable to distinguish between certain colors.
Specific Color Vision Capabilities of Rabbits
Rabbits are most sensitive to blue-violet light, followed by yellow-green light. They are unable to see red light, and they perceive green light as a shade of yellow. This means that rabbits see the world in a very different way than humans do.For
example, a red rose would appear black to a rabbit, and a green leaf would appear yellow. This difference in color vision can affect the way that rabbits interact with their environment. For example, rabbits may be more likely to eat plants that are yellow or green, as they are more visible to them.
Comparative Color Vision
Rabbits possess a distinct color vision system compared to other mammals like humans and dogs. Understanding these differences sheds light on the evolutionary adaptations and ecological niches of various species.
Humans, with their trichromatic vision, can perceive a wide spectrum of colors thanks to three types of cone cells in their retinas. Dogs, on the other hand, have dichromatic vision, relying on two cone cell types, making them less sensitive to certain hues, particularly red and green.
Evolutionary Implications
The differences in color vision among species stem from their evolutionary history and ecological adaptations. Humans’ trichromatic vision is believed to have evolved as a result of their arboreal ancestry, where distinguishing fruits and leaves against a complex background was crucial for survival.
In contrast, dogs’ dichromatic vision may have been advantageous in detecting prey against various terrains.
Applications of Rabbit Color Vision
Rabbit color vision has numerous applications in scientific research, providing valuable insights into various fields.
In medicine, rabbit models have been instrumental in studying color perception disorders, such as color blindness and night blindness. Researchers utilize rabbits to investigate the genetic and physiological basis of these conditions, aiming to develop treatments and improve human health.
Animal Welfare
Rabbit color vision also plays a significant role in animal welfare. Understanding how rabbits perceive colors enables researchers and animal care professionals to design optimal living environments, including proper lighting and color choices for enclosures and feeding areas. This knowledge helps ensure the well-being and comfort of rabbits in captivity.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the topic of rabbit color vision offers a captivating glimpse into the diverse sensory experiences of the animal kingdom. Rabbits, with their dichromatic vision, perceive the world in a unique way, relying on cues such as brightness and contrast to navigate their surroundings.
While they may not experience the full spectrum of colors like humans, their visual adaptations have undoubtedly played a vital role in their survival and evolution. Further research in this field promises to shed even more light on the fascinating visual capabilities of these enigmatic creatures.
FAQ Summary
Can rabbits see color?
Yes, rabbits can see color, but their color vision is different from that of humans. They are dichromats, meaning they have two types of cone cells in their retinas, which allows them to distinguish between blue and yellow.
Are rabbits color blind?
Yes, rabbits are considered color blind in the sense that they cannot see the full spectrum of colors that humans can. They are unable to distinguish between red and green, as well as some shades of orange and brown.
What colors can rabbits see?
Rabbits can see blue, yellow, and shades of gray. They are unable to see red, green, orange, or purple.
How does rabbit color vision compare to human color vision?
Human vision is trichromatic, meaning we have three types of cone cells in our retinas, which allows us to see a wider range of colors. Rabbits, on the other hand, are dichromats, meaning they have only two types of cone cells, which limits their color vision.
What are the implications of rabbit color vision for their behavior?
Rabbit color vision has implications for their foraging behavior. They are attracted to blue and yellow flowers, which they can easily distinguish from the green foliage. Additionally, their dichromatic vision may make it difficult for them to detect predators that are camouflaged in red or green vegetation.